Florida is experiencing a significant surge in Vibrio vulnificus infections, a bacteria capable of causing severe flesh-eating diseases. This alarming increase is linked to recent hurricanes and subsequent flooding, which have created ideal breeding grounds for the bacteria. The Florida Department of Health has reported 74 cases in 2024 alone, a sharp rise compared to the 46 cases reported in 2023. This increase has resulted in a higher death toll as well, with 13 fatalities this year versus 11 last year. Several counties, including Citrus, Hernando, Hillsborough, Lee, Pasco, Pinellas, and Sarasota, have been particularly affected by this outbreak. This underscores the critical importance of understanding this dangerous bacterium, its transmission, and how to mitigate the risks associated with it, especially following severe weather events. The concerning rise in Vibrio vulnificus infections highlights the urgent need for public awareness and preventative measures to safeguard public health.
Understanding Vibrio vulnificus
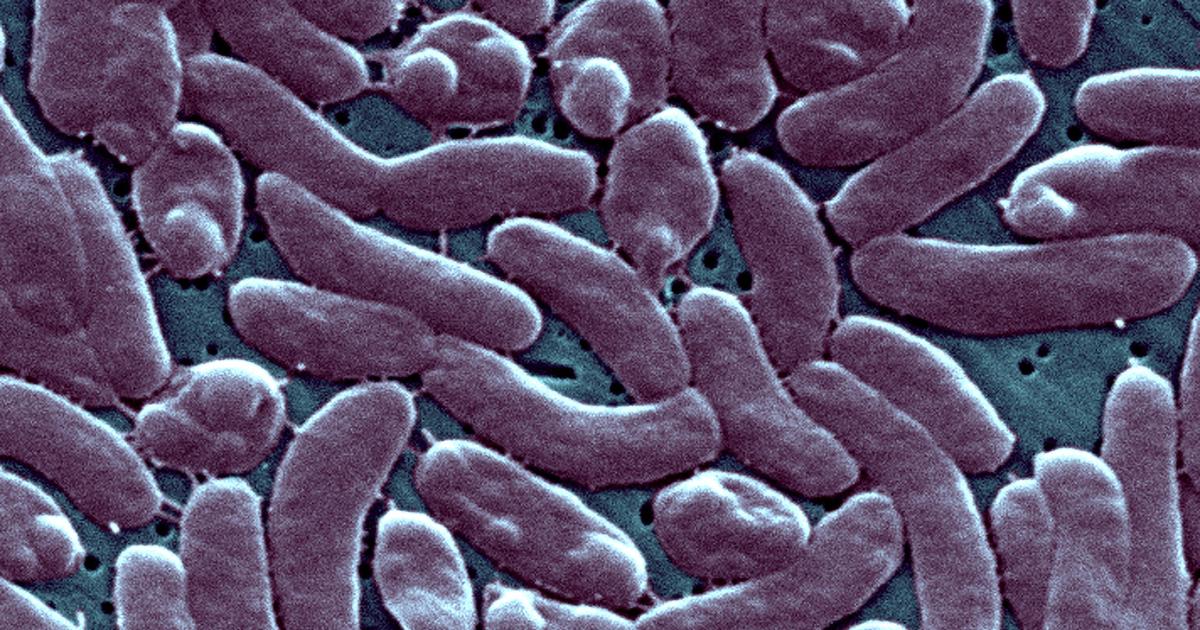
What is Vibrio vulnificus?
Vibrio vulnificus is a naturally occurring bacterium found in warm coastal waters, particularly brackish and saltwater environments. It thrives in warmer temperatures and its concentration increases significantly following periods of heavy rainfall and flooding. Contact with contaminated water can lead to infection, often through ingestion of contaminated seafood or exposure of open wounds to the bacteria-laden water. This bacterium isn’t limited to seawater; floodwaters contaminated with wastewater can also harbor the dangerous pathogen. Understanding this environmental context is vital for effective prevention strategies. The bacteria’s ability to proliferate quickly in disturbed aquatic environments after hurricane activity, as demonstrated by this latest outbreak, makes post-hurricane preventative measures particularly critical.
Transmission and Risk Factors
Infection primarily occurs through two routes: ingestion of raw or undercooked seafood, particularly shellfish, contaminated with Vibrio vulnificus and direct contact between open wounds and contaminated water. Individuals with weakened immune systems, chronic liver disease, or iron overload conditions are at significantly higher risk of developing severe infections, and individuals who spend time in or around affected waters are particularly susceptible during post-hurricane cleanups. The increased risk for immunocompromised individuals highlights the importance of additional protective measures during outbreaks for at-risk populations. The high case numbers reported in coastal Florida counties highlight the vulnerability of these specific areas and the urgency for targeted public health interventions.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Vibrio vulnificus Infection
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of Vibrio vulnificus infection vary widely, depending on the type of infection. Gastrointestinal infections, the most common form, present with symptoms like diarrhea, often accompanied by stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and fever. This milder form of infection, which can be more common following the ingestion of contaminated seafood, while still requiring medical attention can sometimes resolve without severe complications. However, the more dangerous form presents with necrotizing fasciitis. This severe infection rapidly causes the death of tissue surrounding an open wound, often characterized by intense pain, swelling, redness, and blistering at the infection site, along with fever and chills. The fast progression of necrotizing fasciitis underscores the critical importance of immediate medical attention, as delays in treatment drastically decrease survival chances. These systemic symptoms warrant swift diagnosis and antibiotic treatment to prevent potentially fatal outcomes.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you suspect a Vibrio vulnificus infection, immediate medical attention is crucial. Prompt diagnosis through blood, wound, or stool tests are essential. Early diagnosis ensures the appropriate treatment, potentially minimizing tissue damage and death, hence saving limbs and lives. Delays in receiving proper antibiotic treatment can cause the infections to spread rapidly, often demanding extensive surgical intervention and leading to debilitating health problems. The promptness in seeking treatment in the event of these signs and symptoms remains crucial for survival.
Prevention and Treatment of Vibrio vulnificus
Preventive Measures
Several precautions can significantly reduce the risk of Vibrio vulnificus infection. Avoid consuming raw or undercooked shellfish, particularly from potentially contaminated waters. This means carefully inspecting and cooking all shellfish thoroughly before eating. Ensure wounds are properly bandaged and covered to prevent contamination with seawater, especially in areas where the Vibrio vulnificus bacterium might be prevalent. Immediately washing open wounds thoroughly with fresh water and soap after any contact with potentially contaminated water should be practiced. After hurricanes, be wary of flooded waters, since these become breeding grounds for the bacterium. The post-hurricane flooding situation warrants extreme caution, demanding rigorous preventive strategies for those directly involved in cleanup and rescue efforts.
Treatment Options
Treatment primarily involves antibiotics, selected based on the specific type of infection and bacterial resistance profiles. In severe cases, surgery, often including amputation to remove infected tissues, might be necessary to prevent the spread of the bacteria and save the patient’s life. While antibiotics can typically control milder forms of infection, for more severe situations, often in necrotizing fasciitis cases, extensive medical interventions and intensive monitoring become necessary to minimize long-term health implications. The use of intravenous antibiotics and aggressive wound management are critical steps in achieving patient recovery and survival.
Take Away Points:
- Vibrio vulnificus is a serious bacteria that can cause flesh-eating infections.
- Hurricane-related flooding significantly increases the risk of infection.
- Symptoms range from mild gastrointestinal issues to severe necrotizing fasciitis.
- Prompt medical attention and appropriate antibiotic treatment are crucial for survival.
- Prevention strategies include avoiding contaminated water and undercooked seafood.